In this post we’ll get familiarized with Nmap, network mapping tool. It helps to perform a port scan of hosts in a network and to identify the services provided by them. In short, it is a security scanner.
The software provides a number of features for probing computer networks, including host discovery and service and operating system detection. These features are extensible by scripts that provide more advanced service detection, vulnerability detection, and other features. Nmap is also capable of adapting to network conditions including latency and congestion during a scan. Nmap is an opensource tool primarily made for linux systems, released under the GPLv2 license, and is under development and refinement by its user community.
There are a wide array of uses for Nmap. Afew of them are:
- Auditing the security of a device or firewall by identifying the network connections which can be made to, or through it.
- Identifying open ports on a target host in preparation for auditing.
- Network inventory, network mapping, maintenance and asset management.
- Auditing the security of a network by identifying new servers.
- Generating traffic to hosts on a network.
- Find and exploit vulnerabilities in a network.
- Getting NmapIn linux distributions, Nmap can be installed from the terminal. In Ubuntu, you may install using
sudo apt get-install nmap
I have seen GUI version of the tool in Ubuntu Software Center, but I prefer the terminal version. Give it a try if you like. - Run
Nmap is run as a command from the terminal with appropriate switches to obtain the desired outcome. You may refer nmap man pages for the complete list of available switches. As an example, here are a few commands: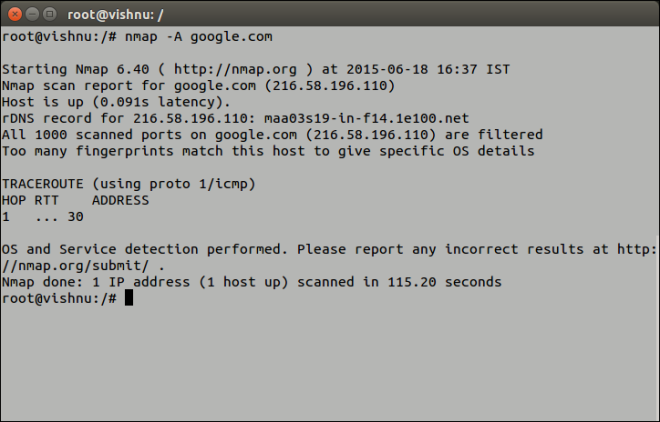
An example run of Nmap - Save and View Scan Report
Scan report can be redirected to a text file for later use. This is done using the –oN switch. The command isnmap -p --oN